Kafka 生产者详解
1. Kafka 消息发送
1.1 数据生产流程解析

- Producer 创建时,会创建一个 Sender 线程并设置为守护线程。
- 生产消息时,内部其实是异步流程; 生产的消息先经过 拦截器 -> 序列化器 -> 分区器,然后将消息缓存在缓冲区(该缓冲区也是在 Producer 创建时创建)。
- 批次发送的条件为: 缓冲区数据大小达到
batch.size或者linger.ms达到上限,哪个先达到就算哪个。 - 批次发送后,发往指定分区,然后落盘到 Broker; 如果生产者配置了
retrires参数大于 0 并且失败原因允许重试,那么客户端内部会对该消息进行重试。 - 落盘到 Broker 成功,返回生产元数据给生产者。
- 元数据返回有两种方式: 一种是通过阻塞直接返回,另一种是通过回调返回。
1.2 必要参数配置
Broker 配置
- 配置条目的使用方式:
- 配置参数:
| 属性 | 说明 | 重要性 |
|---|---|---|
bootstrap.servers | 生产者客户端与 Broker 集群建立初始连接需要的 Broker 地址列表,由该初始连接发现 Kafka 集群中其他的所有 Broker。该地址列表不需要写全部的 Kafka 集群中 Broker 的地址,但也不要写一个,以防该节点宕机的时候不可用。形式为: host1:port1,host2:port2,... . | high |
key.serializer | 实现了接口 org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer 的key序列化类。 | high |
value.serializer | 实现了接口 org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer 的value序列化类。 | high |
acks | 该选项控制着已发送消息的持久性。 acks=0: 生产者不等待 Broker 的任何消息确认。只要将消息放到了 Socket 的缓冲区,就认为消息已发送。不能保证服务器是否收到该消息,retries 设置也不起作用,因为客户端不关心消息是否发送失败。客户端收到的消息偏移量永远是 -1。acks=1: Leader 将记录写到它本地日志,就响应客户端确认消息,而不等待 Follower 副本的确认。如果 Leader 确认了消息就宕机,则可能会丢失消息,因为 Follower 副本可能还没来得及同步该消息。acks=all: Leader 等待所有同步的副本确认该消息。保证了只要有一个同步副本存在,消息就不会丢失。这是最强的可用性保证。等价于 acks=-1。默认值为 1,字符串。可选值: [all, -1, 0, 1] | high |
compression.type | 生产者生成数据的压缩格式。默认是 none (没有压缩)。允许的值: none, gzip, snappy 和 lz4。 压缩是对整个消息批次来讲的。消息批的效率也影响压缩的比例。消息批越大,压缩效率越好。字符串类型的值。默认是none。 | high |
retries | 设置该属性为一个大于 1 的值,将在消息发送失败的时候重新发送消息。该重试与客户端收到异常重新发送并无二至。允许重试但是不设置 max.in.flight.requests.per.connection 为1,存在消息乱序的可能,因为如果两个批次发送到同一个分区,第一个失败了重试,第二个成功了,则第一个消息批在第二个消息批后。int 类型的值,默认: 0,可选值: [0,...,2147483647] | high |
1.3 序列化器
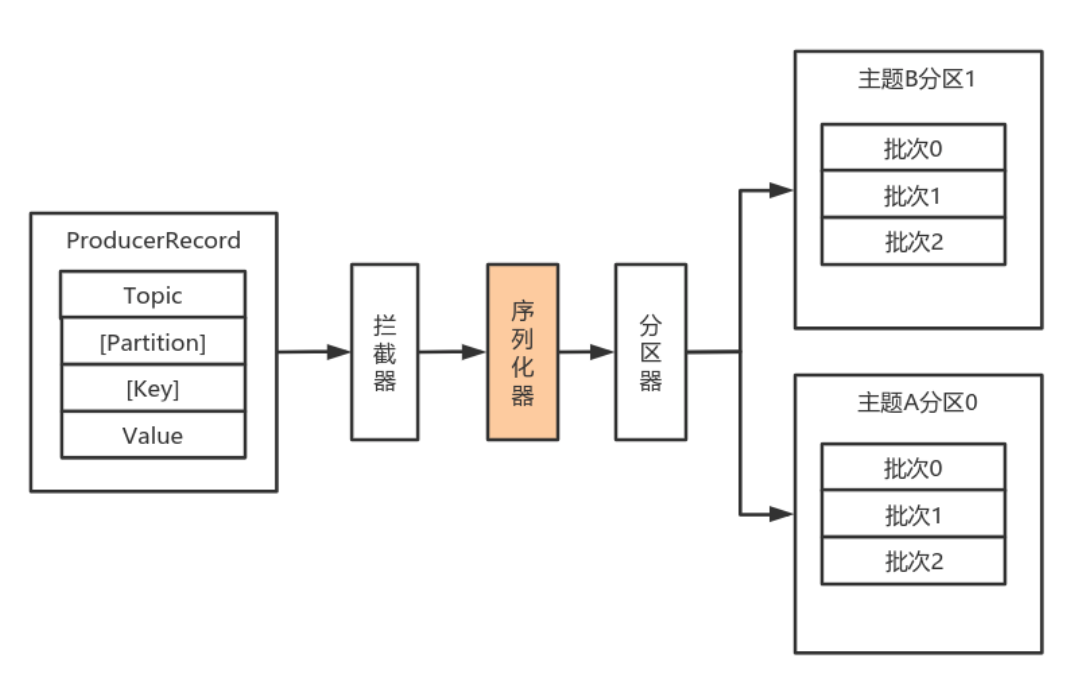
由于 Kafka 中的数据都是字节数组,在将消息发送到 Kafka 之前需要先将数据序列化为字节数组。
序列化器的作用就是用于序列化要发送的消息的。
Kafka 使用 org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer 接口用于定义序列化器,将泛型指定类型的数据转换为字节数组。
/**
* 将对象转换为 byte 数组的接口
*
* 该接口的实现类需要提供无参构造器
*
* @param <T> 从哪个类型转换
*/
public interface Serializer<T> extends Closeable {
/**
* Configure this class.
* @param configs configs in key/value pairs
* @param isKey whether is for key or value
*/
default void configure(Map<String, ?> configs, boolean isKey) {
// intentionally left blank
}
/**
* Convert {@code data} into a byte array.
*
* @param topic topic associated with data (主题名称, associated with ... 与 ... 有关系)
* @param data typed data
* @return serialized bytes
*/
byte[] serialize(String topic, T data);
/**
* Convert {@code data} into a byte array.
*
* @param topic topic associated with data
* @param headers headers associated with the record
* @param data typed data
* @return serialized bytes
*/
default byte[] serialize(String topic, Headers headers, T data) {
return serialize(topic, data);
}
/**
* Close this serializer.
* <p>
* This method must be idempotent as it may be called multiple times. (idempotent 幂等性)
*/
@Override
default void close() {
// intentionally left blank
}
}
系统提供了该接口的子接口以及实现类:
org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteArraySerializerorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ByteBufferSerializerorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.BytesSerializerorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.DoubleSerializerorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.FloatSerializerorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.IntegerSerializerorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializerorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.LongSerializerorg.apache.kafka.common.serialization.ShortSerializer
自定义序列化器
数据的序列化一般生产中使用 avro。
自定义序列化器需要实现 org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.Serializer<T> 接口,并实现其中的 serialize 方法。
代码 略...
1.4 分区器
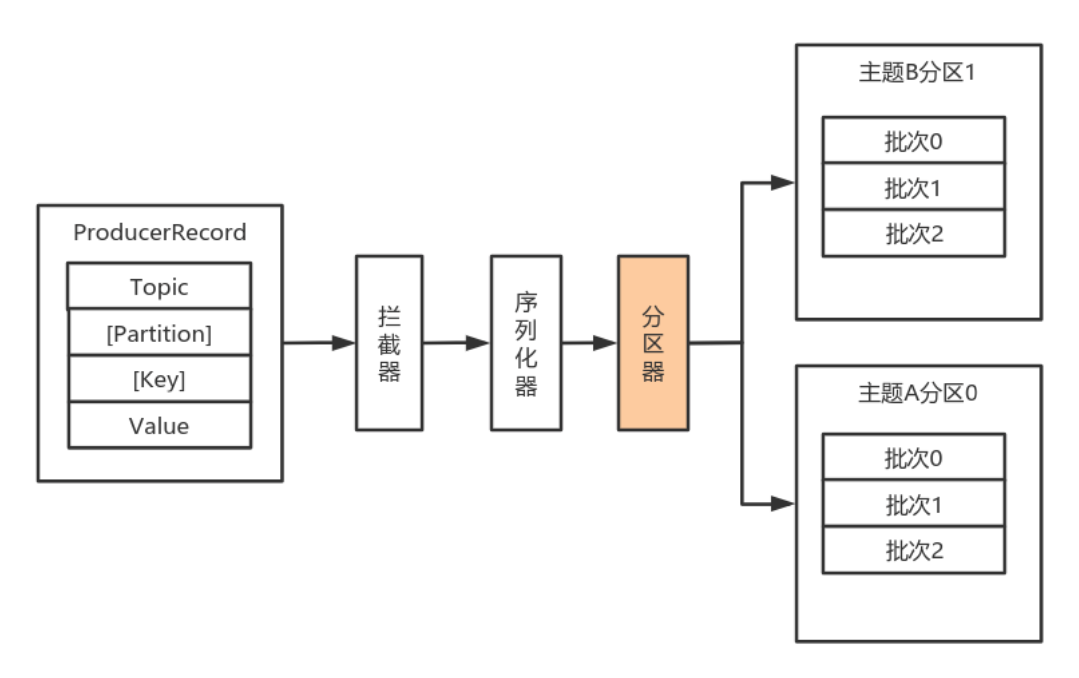
默认(DefaultPartitioner)分区计算:
- 如果 record 提供了分区号,则使用 record 提供的分区号
- 如果 record 没有提供分区号,则使用 key 的序列化后的值的 Hash 值对分区数量取模
- 如果 record 没有提供分区号,也没有提供 key,则使用轮询的方式分配分区号。
源码分析
如果要自定义分区器,则需要:
- 首先开发 Partitioner 接口的实现类
- 在 Kafka Producer 中进行设置:
configs.put("partitioner.class", "xxx.xx.Xxx.class")
位于 org.apache.kafka.clients.producer 包中的分区器接口:
/**
* Partitioner Interface
*/
public interface Partitioner extends Configurable, Closeable {
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes The serialized key to partition on( or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes The serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
*/
int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster);
/**
* This is called when partitioner is closed.
*/
void close();
/**
* Notifies the partitioner a new batch is about to be created. When using the sticky(粘) partitioner,
* this method can change the chosen sticky partition for the new batch.
* @param topic The topic name
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
* @param prevPartition The partition previously(预先的) selected for the record that triggered a new batch
*/
default void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
}
}
包 org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals 中分区器的默认实现:
/**
* The default partitioning strategy:
* <ul>
* <li>If a partition is specified(指定的) in the record, use it
* <li>If no partition is specified but a key is present choose a partition based on a hash of the key
* <li>If no partition or key is present choose the sticky partition that changes when the batch is full. (满了就选相邻的分区 => 轮询)
*
* See KIP-480 for details about sticky partitioning.
*/
public class DefaultPartitioner implements Partitioner {
private final StickyPartitionCache stickyPartitionCache = new StickyPartitionCache();
public void configure(Map<String, ?> configs) {}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes serialized key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
*/
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
return partition(topic, key, keyBytes, value, valueBytes, cluster, cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic).size());
}
/**
* Compute the partition for the given record.
*
* @param topic The topic name
* @param numPartitions The number of partitions of the given {@code topic}
* @param key The key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param keyBytes serialized key to partition on (or null if no key)
* @param value The value to partition on or null
* @param valueBytes serialized value to partition on or null
* @param cluster The current cluster metadata
*/
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster,
int numPartitions) {
if (keyBytes == null) {
return stickyPartitionCache.partition(topic, cluster);
}
// hash the keyBytes to choose a partition
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes)) % numPartitions;
}
public void close() {}
/**
* If a batch completed for the current sticky partition, change the sticky partition.
* Alternately, if no sticky partition has been determined, set one.
*/
public void onNewBatch(String topic, Cluster cluster, int prevPartition) {
stickyPartitionCache.nextPartition(topic, cluster, prevPartition);
}
}
可以实现 Partitioner 接口自定义分区器,然后在生产者中配置。
代码 略...
1.5 拦截器

Producer 拦截器(interceptor)和 Consumer 端 Interceptor 是在 Kafka 0.10 版本被引入的,主要用于实现 Client 端的定制化控制逻辑。
对于 Producer 而言,Interceptor 使得用户在消息发送前以及 Producer 回调逻辑前有机会对消息做一些定制化需求,比如修改消息等。 同时,Producer 允许用户指定多个 Interceptor 按序作用于同一条消息从而形成一个拦截链(interceptor chain)。 Interceptor 实现的接口是 org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerInterceptor,其定义的方法包括:
onSend(ProducerRecord): 该方法封装进KafkaProducer.send方法中,即运行在用户主线程中。Producer 确保在消息被序列化以计算分区前调用该方法。用户可以在该方法中对消息做任何操作,但最好保证不要修改消息所属的 Topic 和分区,否则会影响目标分区的计算。onAcknowledgement(RecordMetadata, Exception): 该方法会在消息被应答之前或消息发送失败时调用,并且通常都是在 Producer 回调逻辑触发之前。onAcknowledgement 运行在 Producer 的 IO 线程中,因此不要在该方法中放入很重的逻辑,否则会拖慢 Producer 的消息发送效率。close: 关闭 Interceptor,主要用于执行一些资源清理工作。
如前所述,Interceptor 可能被运行在多个线程中,因此在具体实现时用户需要自行确保线程安全。另外倘若指定了多个 Interceptor,则 Producer 将按照指定顺序调用它们, 并仅仅是捕获每个 Interceptor 可能抛出的异常记录到错误日志中而非在向上传递。这在使用过程中要特别留意。
自定义拦截器
- 实现
ProducerInterceptor接口 - 在 KafkaProducer 的设置中设置自定义的拦截器
代码 略...
2. Kafka 生产者原理剖析

由上图可以看出 KafkaProducer 有两个基本线程:
- 主线程
负责消息创建,拦截器,序列化器,分区器等操作,并将消息追加到消息收集器 RecodeAccumulator 中;
消息收集器 RecodeAccumulator 为每个分区都维护了一个 Deque<ProducerBatch> 类型的双端队列。
ProducerBatch 可以理解为是 ProducerRecord 的集合,批量发送有利于提升吞吐量,降低网络影响; 由于生产者客户端使用 java.io.ByteBuffer 在发送消息之前进行消息保存,并维护了一个 BufferPool 实现 ByteBuffer 的复用; 该缓存池只针对特定大小(batch.size 指定)的 ByteBuffer 进行管理,对于消息过大的缓存,不能做到重复利用。
每次追加一条 ProducerRecord 消息,会寻找/新建对应的双端队列,从其尾部获取一个 ProducerBatch,判断当前消息的大小是否可以写入该批次中。 若可以写入则写入;若不可以写入,则新建一个 ProducerBatch,判断该消息大小是否超过客户端参数配置 batch.size 的值,不超过,则以 batch.size 建立新的 ProducerBatch, 这样方便进行缓存重复利用; 若超过,则以计算的消息大小建立对应的 ProducerBatch ,缺点就是该内存不能被复用了。
- Sender线程
该线程从消息收集器获取缓存的消息,将其处理为 <Node, List<ProducerBatch> 的形式。Node 表示集群的 Broker 节点。
进一步将 <Node, List<ProducerBatch> 转化为 <Node, Request> 形式,此时才可以向服务端发送数据。
在发送之前,Sender 线程将消息以 Map<NodeId, Deque<Request>> 的形式保存到 InFlightRequests 中进行缓存,可以通过其获取 leastLoadedNode, 即当前 Node 中负载压力最小的一个,以实现消息的尽快发出。
3. Kafka 生产者参数配置补充
- 参数设置方式
- 补充参数
表格
